Serum Creatinine Test: Understanding Its Importance
Introduction
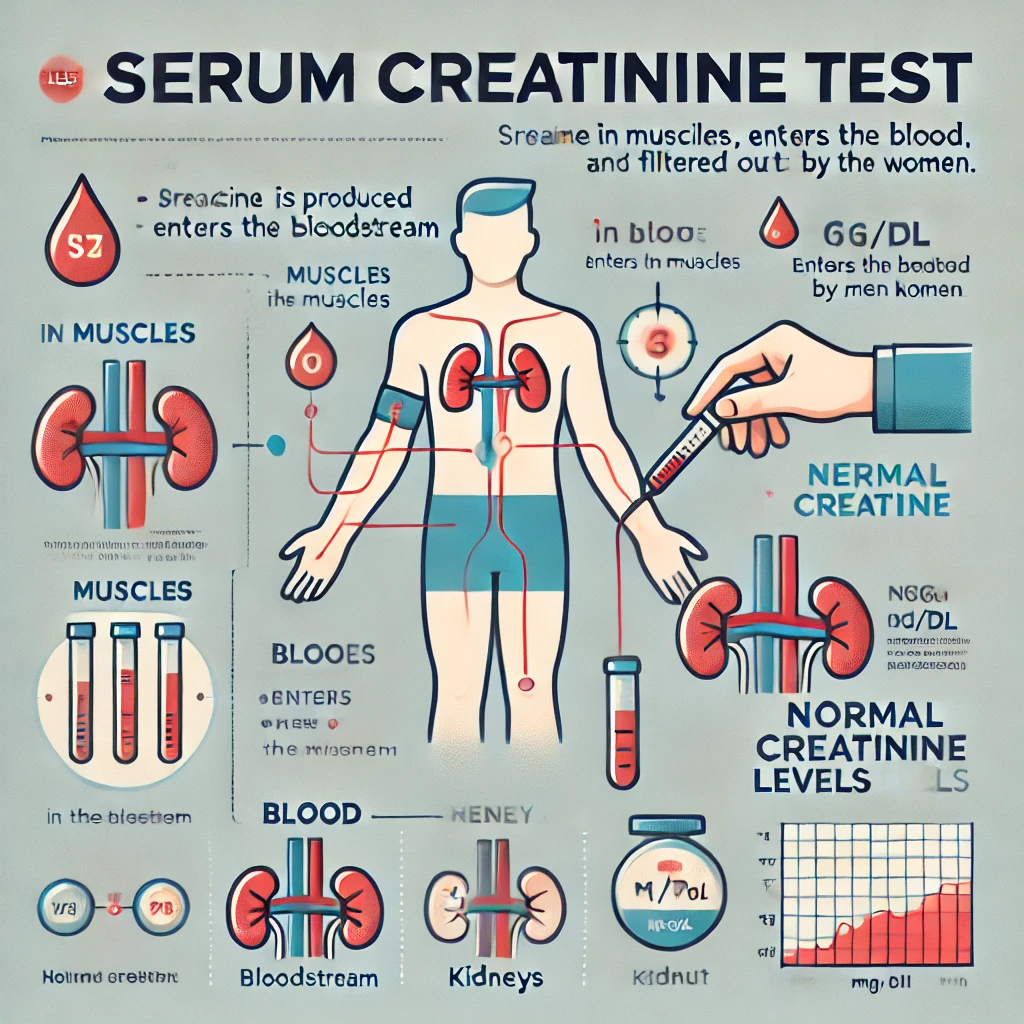
The serum creatinine test is a common blood test that helps doctors evaluate kidney function. Creatinine is a waste product that forms when muscles break down and is filtered out of the blood by the kidneys. High levels of creatinine in the blood may indicate kidney dysfunction or other health concerns.
Why the Serum Creatinine Test is Important
This test is particularly valuable for people at risk of kidney disease, including those with high blood pressure, diabetes, or a family history of kidney issues. It is also a regular part of health monitoring for older adults or patients taking medications that might affect the kidneys.
How Creatinine is Produced and Processed
Creatinine is produced by the normal breakdown of muscle tissue and then released into the bloodstream. The kidneys filter creatinine out of the blood and excrete it through urine. When kidneys are healthy, they keep creatinine at a stable level in the blood. However, if kidney function declines, creatinine levels can rise, alerting doctors to possible issues with kidney health.
What the Serum Creatinine Test Measures
The serum creatinine test measures the amount of creatinine in the blood. Results are typically given in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Healthy ranges may vary slightly based on age, gender, and muscle mass:
- Normal levels for men: 0.6 to 1.2 mg/dL
- Normal levels for women: 0.5 to 1.1 mg/dL
For children, normal ranges may be even lower, depending on their age and growth stage.
Preparing for the Test
This test usually requires a simple blood sample, often taken from the arm. In most cases, no special preparation is needed. However, it’s always best to let your doctor know about any medications or supplements you are taking, as some can impact creatinine levels. If your doctor needs a precise measure, they may ask you to avoid eating protein-heavy foods or strenuous exercise for 24 hours before the test. CLICK HERE FOR SERUM CREATININE TEST————-}}}}}}
Understanding Test Results
If serum creatinine levels are higher than normal, it could indicate kidney issues. However, elevated creatinine can also result from other factors, such as dehydration, high-protein diets, or strenuous exercise.
- Low serum creatinine levels are usually less concerning but can be seen in cases of severe muscle loss, liver disease, or pregnancy.
If your levels are high, your doctor may order further tests to determine kidney function, such as the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) test. The GFR is a more detailed measure of how well your kidneys are filtering waste.
Factors Affecting Creatinine Levels
Several factors can impact creatinine levels, including:
- Age: Older adults tend to have lower creatinine levels due to decreased muscle mass.
- Muscle Mass: Athletes or those with more muscle may have higher creatinine levels, even with healthy kidneys.
- Diet: High protein intake can raise creatinine levels temporarily.
- Medications: Certain medications can elevate creatinine, so always inform your doctor about any medicines or supplements you’re taking.
- Dehydration: When you’re dehydrated, creatinine levels can increase.
Improving Kidney Health and Managing Creatinine
If your serum creatinine levels are high due to kidney issues, your doctor may suggest lifestyle changes or treatments to protect kidney function:
- Hydrate: Drink plenty of water, as dehydration can worsen kidney strain.
- Diet: Eat a balanced diet with moderate protein intake and limit salt to prevent kidney overload.
- Blood Pressure and Diabetes Management: Keeping blood pressure and blood sugar under control can reduce kidney stress.
- Regular Exercise: Moderate, regular exercise supports overall health, including kidney function.
- Medication Review: Consult your doctor to ensure no medications are unnecessarily straining your kidneys.
Conclusion
The serum creatinine test is a quick, effective way to monitor kidney health. By keeping an eye on creatinine levels, you and your doctor can spot potential kidney problems early and take steps to support and protect your kidneys.








Add comment