NB.1.8.1 COVID Variant: Comprehensive Guide to the Emerging Threat
Introduction
The global health landscape is once again under scrutiny with the emergence of a new COVID-19 variant, NB.1.8.1. First identified in January 2025, this variant has rapidly spread across multiple continents. Consequently, health authorities are closely monitoring its progression. This comprehensive guide outlines its origins, spread, symptoms, vaccine efficacy, and preventive measures.
Origins and Classification
NB.1.8.1 is a descendant of the Omicron JN.1 lineage. It was first detected in China in January 2025. Since that time, it has been identified in over 22 countries, including the United States, Australia, and the United Kingdom. Given its rapid spread and potential impact, the World Health Organization (WHO) has labeled it as a “variant under monitoring.”
Spread Across the United States
The NB.1.8.1 variant has now been detected in several U.S. states. These include California, Washington, Virginia, Hawaii, Rhode Island, and New York City. Notably, in California, it rose from 2% of COVID-19 cases in April to 19% by May 1, 2025. Although the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is monitoring the variant, it has not yet appeared in national estimates due to its limited prevalence.
Common Symptoms of NB.1.8.1
Symptoms of NB.1.8.1 resemble those of previous COVID-19 strains and may include:
- Fever or chills
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue and muscle aches
- Headache
- Loss of taste or smell
- Sore throat and congestion
- Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
These symptoms can vary in intensity. However, current data suggests NB.1.8.1 does not lead to more severe illness than earlier variants.
Is NB.1.8.1 More Contagious?
Yes. Several spike protein mutations (T22N, F59S, G184S, A435S, V445H, and T478I) may enhance the variant’s ability to infect human cells. These changes significantly increase NB.1.8.1’s transmissibility compared to other circulating strains. While this may lead to more infections, it does not necessarily result in more severe outcomes.

Vaccine Effectiveness
Current vaccines continue to offer protection against severe disease, hospitalization, and death. The California Department of Public Health reports that vaccines targeting the JN.1 lineage—including the latest boosters—are expected to remain effective. Thus, it is crucial to stay current with vaccination schedules.
How to Protect Yourself and Others
To slow the spread of NB.1.8.1, individuals should consider these precautionary steps:
- Wear masks in crowded or poorly ventilated indoor settings
- Wash hands thoroughly and frequently
- Maintain physical distance where possible
- Avoid large gatherings during periods of high transmission
- Stay up-to-date with vaccinations and boosters
Furthermore, some regions are even debating the reinstatement of mask mandates to further mitigate risk.
Global Impact and Regional Trends
NB.1.8.1 has had a significant impact on healthcare systems in parts of Asia. For instance, in China, the proportion of severely ill respiratory patients with COVID has risen from 3.3% to 6.3% within a month. Similarly, Hong Kong has reported its highest hospitalization rate in 12 months. Emergency room admissions in Taiwan surged by 78% over a single week. These trends highlight the urgency for global vigilance.
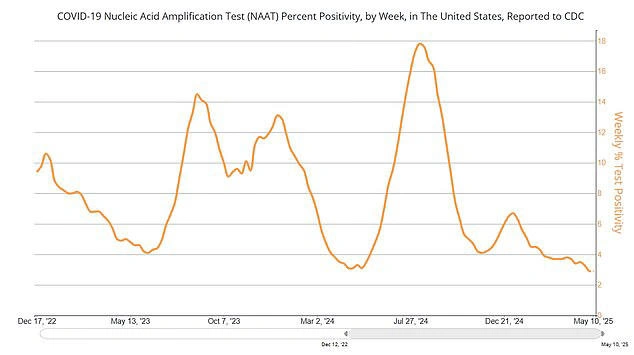
Public Health Outlook
Experts agree that seasonal surges in COVID-19 ( NB.1.8.1 COVID variant ) cases are likely to continue. Monitoring emerging variants and adopting timely preventive measures can effectively reduce transmission. Accordingly, communities are encouraged to stay informed and adapt public health strategies as needed.
Conclusion
NB.1.8.1 is currently considered a variant under monitoring. While it demonstrates higher transmissibility, there is no evidence suggesting increased severity. Vaccination remains a critical defense, and consistent preventive behaviors can make a meaningful difference. Informed communities are better prepared to navigate this evolving health challenge.







Add comment